Welcome to “Tax Planning Essential Strategies for Individuals and Businesses.” This blog explores fundamental concepts and strategies to help you make informed tax decisions. Whether you’re an individual or a business owner, understanding tax planning is crucial for optimizing liabilities and maximizing savings. We’ll cover tax basics, individual and business strategies, and adapting to a changing tax landscape. Join us on this journey to master tax planning and take control of your taxes for a brighter financial future.
How Do You Plan For Taxes?
Tax planning means looking at a financial plan or situation to make sure that everything fits together so that you pay the least amount of taxes possible. A plan is called “tax efficient” if it helps you pay the least amount of taxes possible. Planning for taxes should be an important part of every investor’s financial plan. For success, it’s important to pay less in taxes and put as much as possible into retirement funds.
Fortunately, tax preparation has benefits beyond tax savings. The approach improves money management, reducing spending and increasing profits.
How Tax Planning Strategies Help
Tax planning tactics save people money and help them avoid tax penalties, get the most out of their tax deductions, organize their financial documents, and plan for the future. On the other hand, not planning for taxes takes money away from other important things in life by making tax bills higher than they need to be.
Students in college are especially likely to get tax hits that aren’t fair because their parents can’t name them as dependents on their tax returns and they have to pay back student loans. Here are some of the ways that college students, other people, and businesses can gain from tax planning, as well as some of the things that can go wrong if you don’t do it right.
Tips For Individuals on Tax Planning
The saying “Watch the pennies, and the dollars will take care of themselves” applies twice as much to how people plan their taxes. Tax-saving chances are available to people of all income levels, so college students, recent graduates, and others who are struggling to make ends meet can use them to lower their tax bills. Find out how dependent you are.
The IRS says that a dependent is a qualifying child or qualifying relative:
- A dependent child is a son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister, half-brother, or half-sister who is younger than the tax filer and under the age of 19 at the end of the tax year or under the age of 24 if they are a student.
- A dependent kid must reside with the filer for more than half the year, get more than half of their support from the filer, and not file a joint return unless they want a tax refund.
- A dependent relative must be connected to the filer in one of several ways, live with the filer for the whole year, and make less than $4,200 in gross income for the year.
- The person filing must pay for more than half of the relative’s needs for the year.
For a qualifying kid or qualifying relative to be claimed as a dependent, they must pass three tests:
- Dependent taxpayer test: A taxpayer who is dependent on someone else can’t be dependent on anyone else.
- Joint return test: If a married person files a joint return, no one can claim them as a dependent, unless it’s to get a refund of income tax delayed or an estimated tax payment.
- Citizen or resident test: Except for adopted children, only U.S. Citizens, everlasting residents, U.S. nationals, and Canadian or Mexican residents can be named as dependents.
Learn About Tax Credits For Tuition And Interest Deductions For Student Loans
The IRS describes what makes its AOTC and LLC programs, which give students and their parents education credits, different:
- The AOTC gives credits for things like books, supplies, and equipment that students need for school but that schools don’t pay for. The LLC, on the other hand, only goes to tuition, fees, and other qualified education expenses.
- The AOTC can only be used for four years, but the LLC can be used for as many years as you want.
- The MAGI cap for the AOTC is $80,000 for a single person and $160,000 for a married couple filing jointly. The maximum MAGI for an LLC is $68,000 for individuals and $136,000 for married couples.
- Student loan interest can be deducted up to $2,500 or the amount paid in the year, whichever is less.
As the person’s MAGI gets closer to the annual cap for their filing status, the amount they can deduct goes down and eventually goes away. You can claim the reduction as a change to income without listing all your deductions.
Small Business Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning probably won’t be at the top of a business owner’s list of things to do. But tax planning techniques for small businesses can make the difference between success and failure for both old and new businesses. Here are some things business owners should think about when getting ready to meet their tax responsibilities, whether they do their taxes themselves or hire someone else to do it.
Ways for new businesses to plan for their taxes
Inc. says that new businesses should be aware of the taxes they may have to pay:
- Income taxes: Most companies will also have to pay state income taxes on top of the federal income tax. The taxes practice to C corporations, wherein the enterprise can pay the tax, sole, partnerships, limited liability companies, and S corporations, where the owners pay income taxes.
- Employee taxes: Employers must withhold taxes on salaries and FICA. The company must pay FICA, state, and federal unemployment taxes.
- Sales taxes: Businesses in states with sales taxes must collect the tax from customers at the time of sale. When a business sells goods or services in a state that has a sales tax, it must receive the tax from the customer at the time of the sale. Businesses that don’t receive sales taxes may have to pay fines to the state.
- Excise taxes: Some firms pay excise taxes on fuel, highway use, and other factors.
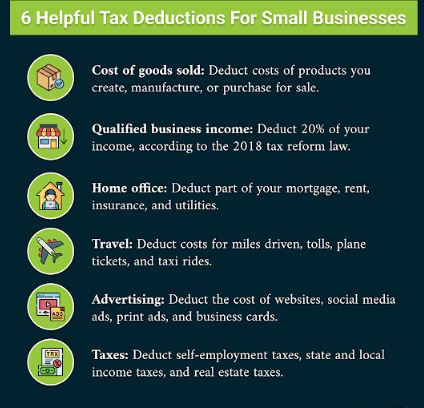
“Cost of goods sold lets you deduct the costs of products you create, make, or buy to sell. Qualified business income lets you deduct 20% of your income, according to the 2018 tax reform law. Home office lets you deduct a portion of your mortgage, rent, insurance, and utilities. Travel lets you deduct the costs of miles driven, tolls, plane tickets, and taxi rides. Advertising, or deducting the cost of web advertising, lets you deduct the cost of web advertising. and taxes, like self-employment taxes, state and local income taxes, and real estate taxes.”
Deductions for Business Property
The IRS lets companies take deductions for rent payments on properties they don’t own, as long as they don’t get ownership or equity in the properties. For home-based businesses, costs like a portion of the mortgage interest, insurance, utilities, repairs, and depreciation can be deducted.
When a private car is used for business, the costs of the vehicle may be able to be deducted from the business’s tax return. Only the work mileage counts toward the deduction, which is based on the number of miles driven and changes from year to year.
Keeping track of income and spending
The IRS tells small businesses and people who work for themselves what kinds of records they need to keep for tax purposes:
- Gross receipts: This group includes tapes from cash registers, information about deposits, receipt books, invoices, and entries on Form 1099-MISC.
- Purchases and expenses: This area has canceled checks and other proofs of payment, cash register tape receipts, bills, and credit card receipts and statements.
- Travel, transportation, entertainment, and gifts fall into this category. The IRS Publication 463 explains how to use the normal mileage rate and other rules for proving deductions in this category.
- Assets: This section tells you about the business’s property, such as when it was bought, how much it cost, how much it cost to fix up, what expenses were taken, how it was used, and how it was gotten rid of (resale price, etc.).
- Employment taxes: The IRS Publication 15 and Employment Tax Recordkeeping says that certain employment tax records must be kept for four years.
Investments In a Pension Plan
The IRS lists the benefits for small business owners who put money into their own and their workers’ retirement plans:
- Businesses can deduct retirement payments from taxable income.
- The assets can grow without having to pay taxes.
- Businesses have a lot of choices about how and when to put money into retirement funds.
- When a business starts a plan, it can get credits that cover some of the costs of putting it into action.
- Employers can find and keep good workers by offering retirement plans.
The IRS has information about the different types of retirement plans and retirement plans for small businesses, such as simplified employee pension (SEP) plans, as well as tips for picking a retirement plan for a small business.
Business Restructuring
The IRS requires businesses to capitalize costs for improvements, but maintenance costs that don’t make the business better, like fixing lights or pipes, can be written off as business expenses. Investopedia says that when a business reorganizes, it must pay a one-time reorganization charge.
Acquisitions, downsizing, moving, combining debt, and writing off assets are common situations in which the restructuring charge is used. Restructuring costs are considered one-time costs for running a business. Costs like starting a new business or buying one are tax-deductible, but reworking costs are only tax-deductible right away if the deal doesn’t go through.
Planned-out tax strategies for small businesses
- Internal Revenue Service, Small Business and Self-Employed Tax Center — Information for people who file Form 1040 or 1040-SR, Form 2106, and Schedule C, E, or F.
- Internal Revenue Service, Deducting Business Expenses: An explanation of all the types of deductions that small companies and people who work for themselves can take.
- Small Business Administration, Tax Planning and Reporting for a Small Business: A guide with a pretest and a self-test for small Business tax planning needs.
Why Tax Planning is Important
Planning is the key for both people and businesses to reach their goals. The amount of money that can be saved by taking steps to pay less in taxes shows how important tax planning is. As a business grows or a person moves up in their job, these steps will change. But careful, smart tax planning is still needed from the beginning to the end.
Strategies that can help you save money on taxes
The faster you see the benefits of a smart tax plan, the sooner you can start making one. Brady Ware Financial Services discusses four tax planning scenarios that are paid handsomely.
- Contribution bunching: By putting together charity donations in the same tax year, people can take itemized deductions in some years and the higher standard deduction in other years. This is called “bunching.”
- 529 plan: Investopedia says that a 529 plan is a tax-advantaged way to save money. There are many different kinds of 529 plans, but the most common ones are tax-deferred savings plans that let you take money out tax-free for approved education costs and prepaid tuition plans that lock in the current tuition rates at colleges and universities that participate.
- Entity organization for people who work for themselves: When a business started by one person is set up as a limited liability company (LLC), the owner is responsible for all taxes. By reorganizing as a flow-through entity like an S corporation, the business escapes being taxed twice. Owners and buyers are taxed on income, not business value.
- Required minimum distributions: If you inherit an individual retirement account and are above 70 and a half, you must take the minimum payout by December 31 of the tax year. A 50% excise tax may apply if a person doesn’t take the whole minimum payout.
How not Making Plans can Increase your Tax Bill
Some people rush around in December to find ways to cut their tax bills for the year. USA.gov gives an overview of recent changes to tax laws, such as which tax breaks are being extended, how tax forms and directions have changed, and how fees and deductions have changed.
- The IRS talks about how the new COVID-19 law affects employment taxes.
- The IRS explains retirement plan changes due to COVID-19.
- Investopedia helps taxpayers plan their taxes for 2020. For example, it tells them if stimulus funds are taxable if tax brackets and rates are changing, and if standard deductions are going up.
- The IRS looks at how recent tax changes affect business customers, like if they need to recalculate their estimated tax payments or if their tax deductions need to be changed or added.
No organization or person can succeed without well-planned tax-cutting strategies. A robust yet adaptable tax plan is crucial. A full and up-to-date tax plan will pay off in many ways today and tomorrow.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, tax planning is a vital aspect for individuals and businesses alike. By implementing essential strategies such as maximizing deductions, making retirement contributions, choosing the right business entity, and understanding timing, you can optimize your tax liabilities and potentially save a significant amount of money.
To explore more in-depth information and gain valuable insights into tax planning, visit our website at Finaccurate. Discover expert advice, resources, and tools to help you navigate the complexities of the tax system and make informed financial decisions. Take control of your taxes and unlock greater financial success today.